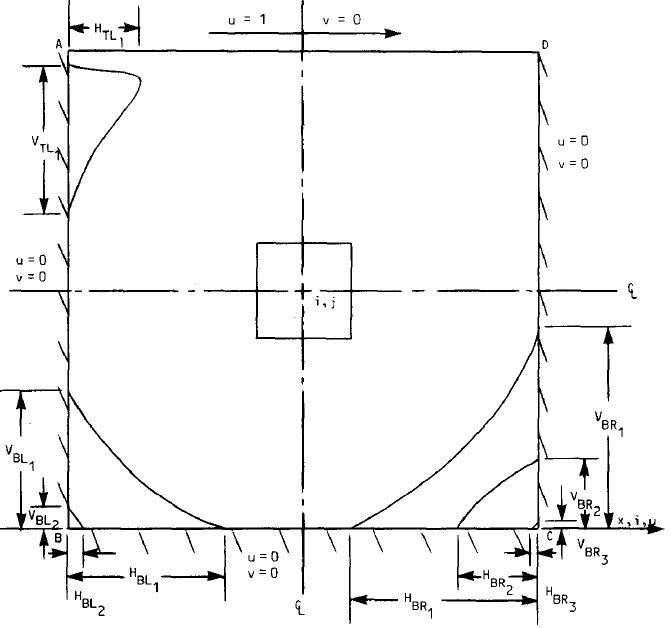
دانلود مقاله High-Re Solutions for Incompressible Flow Using the Navier-Stokes Equations and a Multigrid Method, by U. GHIA, K. N. GHIA, AND C. T. SHIN, 1982
… این محتوا تنها برای اعضای ویژه و سطح مشخص می باشد.ثبت نامAlready a member? از اینجا وارد شوید...
دانلود مقاله Darcy Model for the Study of the Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Around a Cylinder Embedded in Porous Media
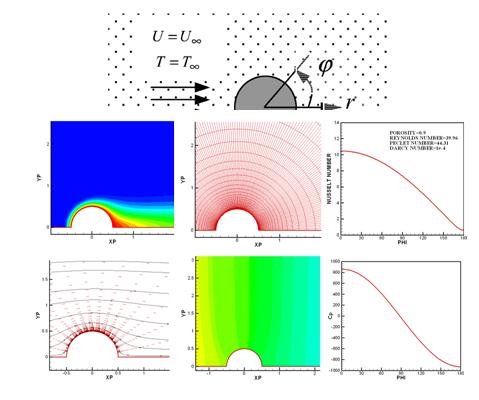
Steady-state convective heat transfer around a circular cylinder
embedded in porous media is studied in the range of low and
moderate Peclet numbers less than 40. The cylinder is at constant
temperature and the Darcy model is used for the analysis of fluid
flow and heat transfer in porous media. The governing equations
are discretised using finite volume approach based on staggered
grids. The powerlaw scheme is used in the numerical solution and
a SIMPLE-like algorithm is developed and used in the solution process.
It is found that the numerical algorithm is sufficiently efficient
in the range of Peclet numbers less than 40. Parametric studies are
done for better understanding of the porous media effects on the
Nusselt number distribution, pressure distribution, and flow and
temperature fields around a circular cylinder. The results are compared
with the available numerical data in the literature and have
shown good agreements.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر استفاده از روغن پلاستیک ضایعاتی در موتورهای دیزل Utilization of waste plastic oil in diesel engines: a review

Disposal of waste plastic accumulated in
landfills is critical from the environmental perspective.
The energy embodied in waste plastic could be
recovered by catalytic pyrolysis as waste plastic oil
(WPO) which could be recycled as a fuel for diesel
engines. This method presents a sustainable solution
for (a) waste plastic management as the gap between
global plastic production and waste plastic generation
keeps widening, (b) replacing diesel partially or
wholly which is currently extracted from fast depleting
fossil crude oil. The present work attempts to bring
together all the investigations pertaining to WPO
usage either (a) as a neat fuel or (b) as a blend
component with diesel or (c) with an oxygenated
additive till date in diesel engines and reviews the
engine’s performance, emission and combustion characteristics.
Majority of the works utilised WPO
extracted from mixed waste plastic as a feedstock
using a laboratory scale batch reactor via catalytic
pyrolysis. Silica, Alumina, ZSM-5 and Kaolin were
used as catalysts. This method often yielded up to 80%
of liquid WPO. This oil had a slightly lower cetane
number than fossil diesel and hence produced longer
ignition delays and higher heat releases during
premixed combustion phasing. NOx emissions were
higher with WPO which is addressed by modifying the
injection timing or by means of EGR. Contrary to
popular belief, smoke emissions are mostly lower with
WPO and could be brought down further to Euro
levels by the use of oxygenated additives. In summary,
WPO was found to run smoothly in diesel engines and
more work is necessary to study the PM characterisation
and long-term durability of the engine when
fueled with this oil.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر استفاده از هیدروژن در موتورهای احتراق داخلی (گازوئیل-گاز مایع -دیزل) از دیدگاه عملکرد احتراقی A review ازof hydrogen usage in internal combustion engines (gasoline-Lpg-diesel) from combustion performance aspect

Demand for fossil fuels is increasing day by day with the increase in industrialization and
energy demand in the world. For this reason, many countries are looking for alternative
energy sources against this increasing energy demand. Hydrogen is an alternative fuel with
high efficiency and superior properties. The development of hydrogen-powered vehicles in
the transport sector is expected to reduce fuel consumption and air pollution from exhaust
emissions. In this study, the use of hydrogen as a fuel in vehicles and the current experimental
studies in the literature are examined and the results of using hydrogen as an
additional fuel are investigated. The effects of hydrogen usage on engine performance and
exhaust emissions as an additional fuel to internal combustion gasoline, diesel and LPG
engines are explained. Depending on the amount of hydrogen added to the fuel system, the
engine power and torque are increased at most on petrol engines, while they are decreased
on LPG and diesel engines. In terms of chemical products, the emissions of harmful
exhaust gases in gasoline and LPG engines are reduced, while some diesel engines increase
nitrogen oxide levels. In addition, it is understood that there will be a positive effect on the
environment, due to hydrogen usage in all engine types.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر فناوریهای کاهش آلودگی برای موتورهای دیزل وسایل دریایی با سرعت کم و متوسط و پتانسیل آنها برای بازیافت حرارت اتلافی A review of emissions reduction technologies for low and medium speed marine Diesel engines and their potential for waste heat recovery

Reducing emissions from internal combustion engines is becoming one of the most important tasks for engine
manufactures and transport regulatory organizations. In particular, the marine transportation sector is one of the
most polluting, due to the intense maritime activity and the use of low-quality fuels, burned in Heavy Duty Diesel
Engines, for ship propulsion and auxiliary power generation. In order to reduce the global shipping environmental
impact, the IMO (International Maritime Organization) is restricting NOx and SOx ships’ emissions through the
introduction of the IMO Tier III legislation, which requires to consider a wide spectrum of emissions reduction
technologies and strategies, which are going to have an impact on the engine performance and fuel consumption.
In this work, the main solutions being currently developed or adopted for low and medium speed Diesel
engines have been reviewed from a qualitative, and sometimes quantitative, point of view, but, in comparison to
previous literature, focusing more on their potential with respect to possible waste heat recovery systems utilization,
such as, in particular, steam Rankine cycles and Organic Rankine Cycles (ORC). Indeed, even though
many of the considered emissions mitigation technologies lead to a certain amount of penalty in fuel economy,
the use of waste heat recovery systems to recover wasted engines energy could become interesting in order to
develop more efficient but, at the same time, cleaner engines.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر تاثیر سوخت بیو دیزل بر طول عمر موتورهای اشتعال جرقه ای Impact of Bio-diesel fuel on Durability of CI Engines – A Review

Bio-diesel is a sustainable, renewable and alternate fuel for CI Engines. The
use of bio-diesel produces various durability issues on key components of CI engines.
For durability studies, the aspects considered are injector coking, carbon deposition on
piston, lubricity of engine oil, wear and tear of piston and cylinder walls and corrosion
of engine parts they come in contact with fuel. In this work, reports about the durability
aspects, published by highly rated journals in scientific indexes, have been cited. From
these reports, the effect of bio-diesel on engine durability are surveyed and analysed.
The use of bio-diesel leads to injector coking, increased carbon deposition on piston,
decreased viscosity of the lubricating oil and fuel dilution, increased engine wear and
increased corrosion.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر مقررات، وضعیت کنونی، اثرات و راهکارهای کاهش آلودگیهای موتورهای دیزلی دریایی A review on regulations, current status, effects and reduction strategies of emissions for marine diesel engines

Marine diesel engines, which provide main power source for ships, mainly contribute to air pollution in ports
and coastal areas. Thus there is an increasing demand on tightening the emission standards for marine diesel
engines, which necessitates the research on various emission reduction strategies. This review covers emission
regulations and emission factors (EFs), environmental effects and available emission reduction solutions for
marine diesel engines. Not only the establishment of the emission control areas (ECAs) in the regulations but also
many experiments show high concerns about the sulfur limits in fuels, sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides
(NOx) emissions. Research results reveal that NOx emissions from marine diesel engines account for 50% of total
NOx in harbors and coastal regions. Sulfur content in fuel oil is an important parameter index that determines
the development direction of emission control technologies. Despites some issues, biodiesel, methanol and liquefied
nature gas (LNG) play their important roles in reducing emissions as well as in replacing fossil energy,
being promising fuels for marine diesel engines. Fuel-water emulsion (FWE) and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
are effective treatment option for NOx emissions control. Common rail fuel injection is an effective fuel injection
strategy to achieve simultaneous reductions in particulate matter (PM) and NOx. Selective catalytic reduction
(SCR) and wet scrubbing are the most mature and effective exhaust aftertreatment methods for marine diesel
engines, which show 90% De-NOx efficiency and 95% De-SOx efficiency. It can be concluded that the integrated
multi-pollutant treatment for ship emissions holds great promise.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر استراتژیهای مختلف برای صرفه جویی در مصرف انرژی سیستمهای تهویه مطبوع A review of different strategies for HVAC energy saving

Decreasing the energy consumption of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems is
becoming increasingly important due to rising cost of fossil fuels and environmental concerns. Therefore,
finding novel ways to reduce energy consumption in buildings without compromising comfort and
indoor air quality is an ongoing research challenge. One proven way of achieving energy efficiency in
HVAC systems is to design systems that use novel configurations of existing system components. Each
HVAC discipline has specific design requirements and each presents opportunities for energy savings.
Energy efficient HVAC systems can be created by re-configuring traditional systems to make more strategic
use of existing system parts. Recent research has demonstrated that a combination of existing air
conditioning technologies can offer effective solutions for energy conservation and thermal comfort. This
paper investigates and reviews the different technologies and approaches, and demonstrates their ability
to improve the performance of HVAC systems in order to reduce energy consumption. For each strategy, a
brief description is first presented and then by reviewing the previous studies, the influence of that
method on the HVAC energy saving is investigated. Finally, a comparison study between these
approaches is carried out.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر ملزومات سیستمهای تهویه در مقررات انرژی ساختمان A review of HVAC systems requirements in building energy regulations

Building energy regulations, also referred to as building energy codes, emerged in the 1970s as an essential
tool for improving energy efficiency and minimising energy consumption in buildings. Basically they aim
at setting minimum energy efficiency requirements to achieve energy efficient design in new buildings.
This paper analyses the development of building energy codes concerning Heating, Ventilation and Air-
Conditioning (HVAC) energy efficiency, along with their scope and compliance paths. The paper focuses on
the synthesis of energy efficiency requirements on HVAC systems of non-residential buildings in different
regulations. Critical issues for the development of prescriptive and performance regulatory paths for this
type of systems in non-residential buildings are discussed in order to improve the understanding of HVAC
energy efficiency topics and to provide policy makers with a menu of options to strengthen the HVAC
section of building energy codes.
دانلود مقاله مروری بر اجزاء یک سیستم تهویه مطبوع با جریان مبرد متغیر برای کاربردهای خانگی A Review of Variable Refrigerant Flow HVAC System Components for Residential Application

A variable refrigerant flow (VRF) classification is a multi-split Heating, Ventilation and Air
Conditioning (HVAC) system that controls refrigerant flow to control separable zones to
residential consumer’s needs. VRF specific components regulate refrigerant flow control for
system performance and reliability. The objective of this review is to recognize the VRF system
components that affect various aspects of operation and performance. The investigate of
preceding experimentation will better assist in the direction of future progress as development of
expansive residential VRF systems are still in primary phases. Findings show that specific testing
through different compressor arrangements, electronic expansion valve (EEV) positioning, and
air flow operations affect performance and thermal comfort. The system responsiveness and
sensitivity are related to the quantity of indoor evaporators that are connected to the system.